Get started
Ploosh is open source yaml based framework used to automatized the testing process in data projects.


Ploosh is open source yaml based framework used to automatized the testing process in data projects.

Ploosh is an innovative testing framework designed to automate the validation processes in your data projects. Built around YAML configuration, Ploosh allows you to quickly compare datasets and ensure they meet expected results, all with minimal code.
With lots of unique blocks, you can easily build a page without coding. Build your next landing page.
Install the ploosh package from PyPi package manager with the following command
pip install ploosh
Add a yaml file with name “connections.yml” and following content:
mssql_getstarted:
type: mysql
hostname: my_server_name.database.windows.net
database: my_database_name
username: my_user_name
// using a parameter is highly recommended
password: $var.my_sql_server_password
Add a folder “test_cases” with a yaml file with any name. In this example “example.yaml”. Add the following content:
Test aggregated data:
options:
sort:
- gender
- domain
source:
connection: mysql_demo
type: mysql
query: |
select gender, right(email, length(email) - position("@" in email)) as domain, count(*) as count
from users
group by gender, domain
expected:
type: csv
path: ./data/test_target_agg.csv
Test invalid data:
source:
connection: mysql_demo
type: mysql
query: |
select id, first_name, last_name, email, gender, ip_address
from users
where email like "%%.gov"
expected:
type: empty
ploosh --connections "connections.yml" --cases "test_cases" --export "JSON" --p_my_sql_server_password "mypassword"
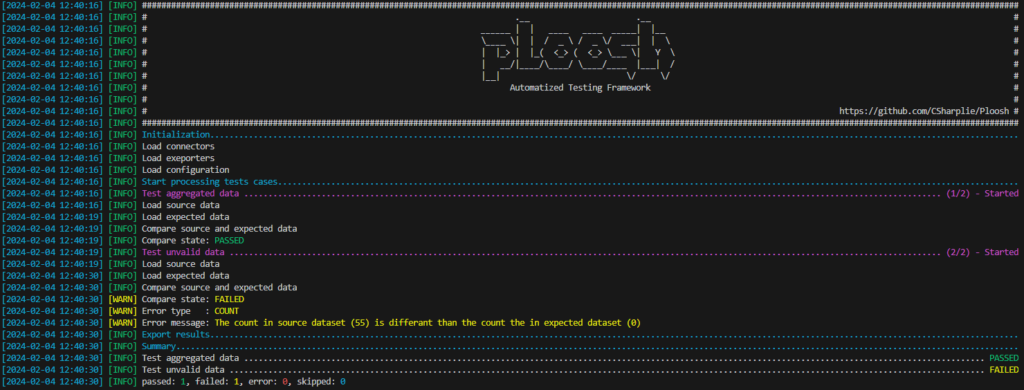
[
{
"name": "Test aggregated data",
"state": "passed",
"source": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 0.0032982
},
"expected": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 6.0933333333333335e-05
},
"compare": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 0.00046468333333333334
}
},
{
"name": "Test invalid data",
"state": "failed",
"source": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 0.00178865
},
"expected": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 1.49e-05
},
"compare": {
"start": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"end": "2024-02-05T17:08:36Z",
"duration": 1.8333333333333333e-07
},
"error": {
"type": "count",
"message": "The count in source dataset (55) is different than the count in the expected dataset (0)"
}
}
]
It’s possible to run the tests with spark. To do that, you need to install the spark package or use a platform that already has it installed like Databricks or Microsoft Fabric.
See the Spark connector for more information.